Electric cars and vehicles are increasingly becoming a cornerstone of the planet's future. While the Green Movement's push to reduce carbon emissions has been a significant driver, advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, and the increasing range of EVs are also propelling their adoption. Modern electric vehicles, which trace their origins back to Thomas Parker's 1884 lead-acid battery version, are now more efficient and accessible than ever.
Regulatory pressures on emissions standards in regions like Europe, China, and parts of North America are key drivers of electric vehicle (EV) sales growth. These pressures, along with advancements in battery technology (leading to increased range and faster charging) and growing consumer interest in sustainability, are accelerating the transition to EVs. Many countries have announced plans to phase out the sale of new gasoline-powered vehicles in the coming decades.

Above (l. to r.), electric car models Tesla Model 3 and Tesla Model X
How the car industry categorizes electric and hybrid cars and vehicles
While this article focuses primarily on all-electric vehicles (EVs), it's important to note that hybrid cars and plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) serve as a transitional stage toward full electrification. Recent advancements in hybrid technology have led to PHEVs with extended electric-only ranges, making them a more viable option for many consumers.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) typically run on electric power until the battery is depleted, at which point they switch to an internal combustion engine (ICE). Recent advancements have extended their electric-only ranges. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCEVs) use electricity generated from hydrogen to power an electric motor, with recent improvements in fuel cell efficiency making them more competitive.
The Hybrid Electric Vehicles takes no plug-in charging, but instead are powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, which uses energy stored in batteries. The battery is charged through regenerative braking and by the internal combustion engine. There also might be an option for an additional smaller engine to be onboard due to the resulting electric power generation made available.
Electric cars can fall into the category of road vehicle that also includes plug-in hybrid, hybrid electric, hydrogen fuel cell, that are a technological departure from the gasoline-powered engine. This article will address electric cars and reference electric vehicles at certain points.
Electric car buyers see their selection as a way to help the planet
Concern about climate change is at an all-time high, and the impact of fossil fuels vehicles and their emissions has become a matter of pressing urgency to even everyday civilians and consumers. Electric vehicles are increasingly viewed as a way to diminish and possibly reverse the harm that happens through climate change. In a 2018 Consumer Reports survey, 80% of those who intend to make an EV their next vehicle purchase cited environmental concerns as their primary motivator.
Norway, a pioneer of sorts of the electric vehicle industry, has diverted consumers and local governments toward battery power using a variety of policies. It offers strong tax incentives for the purchase or lease of EVs, and it subsidizes the construction of private and public charging infrastructure (more on that later).
Norway has been a pioneer in EV adoption, driven by strong government incentives and a focus on renewable energy. However, while Norway still boasts a high EV market share, other countries, particularly in Europe and China, have seen rapid growth. China is now the world's largest EV market by volume, fueled by a combination of government support, domestic manufacturing, and increasing consumer demand.
Government incentives, including tax credits and rebates, play a crucial role in encouraging EV adoption. In the US, the Inflation Reduction Act has restructured the federal tax credit for EVs, making it dependent on factors like vehicle assembly location and battery sourcing. These incentives aim to reduce the upfront cost of EVs and make them more competitive with gasoline-powered cars.
View resources and accessories for electric cars and vehicles from Amazon
The Role of Subsidies and Tax Credits in EV Growth
Many countries offer tax credits and subsidies to encourage EV purchases, although some of these incentives are gradually being phased out. Here are some notable incentives as of 2023:
- USA: Federal tax credit of up to $7,500 (subject to manufacturer sales caps and domestic content requirements)
- Germany: Up to €6,000 in purchase incentives, plus tax exemptions
- France: Ecological bonuses of up to €7,000 for private electric cars
- UK: EV grant of up to £2,500 and exemption from road tax
- China: Phasing out subsidies but offering tax exemptions
- Norway: EVs remain exempt from the 25% VAT on motor vehicles
Consumers are encouraged to check with their local dealerships for up-to-date incentive programs, as policies vary by region.
Countries Phasing Out Internal Combustion Vehicles
Governments worldwide have set ambitious deadlines to end the sale of new gasoline and diesel vehicles:
- 2025: Norway (ban on new gasoline and diesel vehicle sales)
- 2030: European Union, United Kingdom, Canada, Ireland, Israel, Netherlands, India (conditional on economic feasibility)
- 2035: California, Japan, Taiwan
- 2040: China, Germany (under consideration), United States (net-zero emissions goal)
Burning questions and concerns consumers may have regarding EVs
People show ample concern through the questions they have about a new innovation such as electric cars, how they function, and the best ways to use them, etc. But as in most technologically-driven fields answers to such questions are evolving and morphing, due to the state of the technology in place at that particular moment in time. So a checklist of considerations and metrics and benchmarks on electric vehicles would need to be revamped every so often.
Expect a changing technological backdrop and evolutionary advancements due to scientific breakthroughs in ways that could not be foreseen that comes over time. Let's provide a quick answer to a simple question right now. Why don't electric cars have solar panels? The answer would be it would take far too long (with present technology at this writing) to fully charge to 100% since the area required for even just 0.5kW of power would be larger than than the electric cars' entire surface area would provide. Nonetheless, here are some typical questions that are likely to crop up regarding the practicality of purchasing an electric car while the technology is in its relative infancy.
QUESTION: Who are the manufacturers of electric cars and what are their price tags?
ANSWER: The electric vehicle market has expanded rapidly, with established automakers and new entrants offering a wide range of models. Major manufacturers include Tesla, Ford, GM, Hyundai/Kia, Volkswagen Group, and many others. Pricing varies significantly depending on the model, features, and battery range. It's best to consult manufacturer websites and automotive publications for current pricing information.
QUESTION: How Much Electricity Does An Electric Car Use?
ANSWER: An EV's electricity consumption depends on factors like driving style, terrain, and weather conditions. The efficiency is measured in kilowatt-hours per mile (kWh/mile).
QUESTION: How Far Can An Electric Car Go?
ANSWER: Modern EVs offer significantly improved range, often exceeding 200-300 miles. Charging infrastructure has also expanded considerably. Google Maps and other apps provide real-time information on charging station availability and locations.
QUESTION: How Long Do Electric Cars Take To Charge?
ANSWER: DC fast chargers can now deliver much higher power outputs, significantly reducing charging times. Tesla's Supercharger network continues to expand, and other charging networks are also investing in fast-charging infrastructure.
QUESTION: Can you take very long-distance trips in an electric car?
ANSWER: Long-distance EV trips are becoming increasingly feasible thanks to expanding charging networks. Tools like Google Maps can help plan routes and locate charging stations.
QUESTION: What is the expected lifetime of the battery (and car) before it needs replacing?
ANSWER: EV batteries are designed to last for many years. Most manufacturers offer warranties of 8 years or more. Battery lifespan can be affected by factors like extreme temperatures and frequent fast charging.
QUESTION: What does it cost to charge an electric car and what are the company or trademark names of these charging outlets?
ANSWER: In quite a number of cases charging is free, although it would be fair to assume that fees would be attached to premium faster-charging services. 90% or more of level two chargers are absolutely free (USA). Level 3 chargers can sometimes be free. These are factors that might also be controlled depending on what part of the world you are in. Charging station operators that have been in operation include Blink, Electrify America, Greenlots, EvGo (RESEARCH GLOBAL CHARGE STATIONS), but this list is certain to grow as the industry gains traction.
Focus on the electric car battery, expected driving range, and worldwide charging stations
Similar to a conventional auto's gas gauge the majority of electric cars are fitted with a dashboard display of expected range. This may take into account many factors of how the vehicle is being used, and what the battery is powering. However, since factors can vary over the route, the estimate can vary from the actually achieved range.
The display allows the driver to make informed choices about driving speed (a factor in battery drain) and whether to stop at a charging point en route. Some companies have been experimenting with battery swapping to eliminate delay rather than charging. Some roadside assistance organizations offer charge trucks to recharge electric cars in case of emergency.
Perhaps of greatest concern to operating efficiency, today's EVs generally have a shorter range (per charge) than comparable conventional vehicles have (per tank of gas). Of course, it is assumed that the average day to day use of a car does not surpass 200 miles. So overnight charging at a 110-volt outlet could serve most needs. Naturally, you can expect battery and charging technology to adapt and improve over time.
The efficiency and driving range of EVs vary substantially based on driving conditions. Extremely cold or hot outside temperatures tend to reduce driving range since more energy must be used to heat or cool the cabin. High driving speeds reduce range because of the energy required to overcome increased drag. Compared with gradual acceleration, rapid acceleration reduces range. Hauling heavy loads or driving up significant inclines also reduces range.
Finding charging stations, their usage, and using Google Maps to do this
Within each major region of the world, electric car charging stations are essentially universal across car and charger brands, and plugging in a charger into an electric car will charge the car at the fastest rate that car and charger can support. A notable exception is Tesla cars (majority owner Elon Musk) and charging stations, which use their own proprietary chargers, but adapters costing a few hundred dollars can grant access to around 75% of non-Tesla stations. The adapters may also allow non-Tesla vehicles to charge at some Tesla stations other than level 3 Superchargers, assuming Tesla does not try to prevent it.
View EV charging stations on Google Maps
Here is an explanation on using the Google Maps app from your smartphone to locate global electric car charging stations and their real-time availability. Below this paragraph is a custom Google Map from Open Charge Map, a non-commercial, non-profit service working with the global community to develop and provide a public, free, open database of charging equipment locations worldwide. Depending on what country or region of the world you are in you can enter the location data to the Google Maps search slot below to find a charging station nearest you wherever you may be.
Charging stations will have a variety of different speeds, with slower charging being more common for home charging ports, and more powerful charging stations found on public roads and designated areas that can be found using app and mapping tools like Google Maps. The BMW i3 is known to charge from 0–80% of the battery in less than 30 minutes plugged into rapid charging mode. The superchargers developed by Tesla Motors provided up to 130 kW of charging, allowing a 300-mile charge in about an hour. Of course, these are benchmarks that could very well have changed by the time you read this article.
Top electric vehicle manufacturers
The EV market is highly competitive. Leading manufacturers include Tesla, BYD, Volkswagen Group, General Motors, Ford, Hyundai/Kia, and many others. Numerous new EV brands have also emerged.
Stay up-to-date on the latest EV news and developments by following reputable automotive publications and websites specializing in electric vehicles. Refer to the news feeds at this link for the incoming electric car and vehicle news and information.
The Future of EV Technology
Battery technology is advancing rapidly, with new solid-state batteries promising greater energy density, faster charging, and longer lifespans. Additionally, wireless charging technology is in development, potentially eliminating the need for traditional plug-in charging.
Governments and private companies also invest in infrastructure expansion, ensuring that charging stations become as ubiquitous as gas stations. In Norway and the Netherlands, for example, EV owners can find a charging station within a 3-mile radius almost anywhere in the country.
The electric vehicle revolution is accelerating, driven by environmental concerns, government policies, and technological advancements. While challenges such as charging infrastructure and battery production remain, ongoing innovations and market growth ensure that EVs will play a dominant role in the future of transportation. As new developments arise, staying informed will help consumers make the best decisions for their mobility needs.
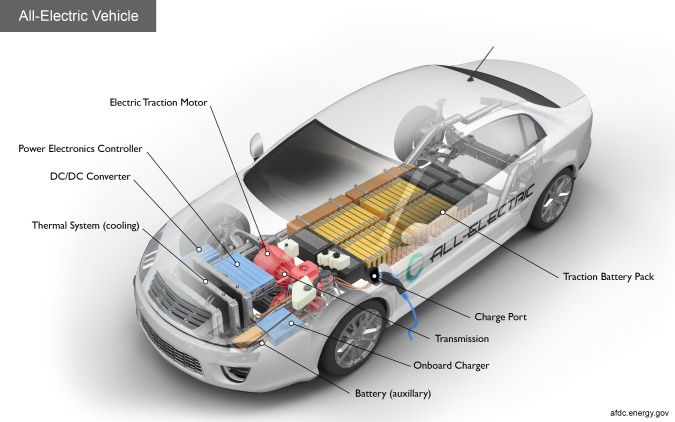
Electric vehicle tech terms to know
Battery - In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to power vehicle accessories.
Battery Degradation - a term used to identify loss of battery storage.
BEV - Battery Electric Vehicle
Brake Regeneration - is a term used when your vehicle puts electricity back into the battery by methods such as brakes.
Charge Port - The charge port allows the vehicle to connect to an external power supply in order to charge the traction battery pack.
DC/DC Converter - This device converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Driving Range - how far an electric vehicle can travel at its current state of charge.
Electric Traction Motor - Using power from the traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle's wheels. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and regeneration functions.
GOM (guess-o-meter) - refers to the driving range in an electric vehicle.
HEV - hybrid electric vehicles
ICE - Internal combustion engine
Kilowatt Hours (kWh) - a measure of electrical energy equivalent to a power consumption of 1,000 watts for 1 hour.
Onboard Charger - Takes the incoming AC electricity supplied via the charge port and converts it to DC power for charging the traction battery. It monitors battery characteristics such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge while charging the pack.
Power Electronics Controller - This unit manages the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery, controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces.
PHEV - Plugin hybrid electric vehicles
Powertrain - The mechanism that transmits the drive from the engine of a vehicle to its axle, or a vehicle's main components that generate power and deliver it to the road surface.
Thermal System (cooling) - This system maintains a proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components.
Traction Battery Pack - Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
Transmission (electric) - The transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
Top Off - As it relates to battery charging, you add to the residual charge in your EV battery rather than waiting for it to drain down close to 0% before recharging.
_______________________________
SOURCES:
How much do electric cars cost? (EnergySage website)
https://www.energysage.com/electric-vehicles/costs-and-benefits-evs/electric-car-cost/
Nine countries say they’ll ban internal combustion engines. So far, it’s just words. By Michael J. Coren (Quartz, August 7, 2018)
https://qz.com/1341155/
How Do All-Electric Cars Work? (U.S. Department of Energy website)
https://afdc.energy.gov/vehicles/how-do-all-electric-cars-work
The Race For The Electric Car (CB Insights Technology Market Intelligence website)
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/report/electric-car-race/
25 Questions About Electric Cars (Answered) (Avto Wow website)
https://avtowow.com/25-electric-car-questions
Special Report: The Electric Car Comes of Age. By Jon Linkov (Consumer Reports, August 8, 2019)
https://www.consumerreports.org/hybrids-evs/electric-car-comes-of-age/
wattEV2Buy Electric Car List (wattEV2Buy website)
https://wattev2buy.com/electric-vehicles/
Global Electric Vehicle Market Outlook Report 2019-2025 - ResearchAndMarkets.com (AP press release content from Business Wire, April 9, 2019)
https://www.apnews.com/22912b0992924ddca1757eea6795bc1f
List of electric cars currently available (Wikipedia website)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_electric_cars_currently_available
Global EV Outlook 2019 (IEA website, May 27, 2019, Paris)
https://www.iea.org/publications/reports/globalevoutlook2019/
Can you save money and the planet by owning a Tesla or another electric car? By Lorie Konish (CNBC: Impact Investing, April 16, 2019)
https://www.cnbc.com/2019/04/12/can-you-save-money-and-the-planet-by-owning-an-electric-car.html
Electric Car Price Tag Shrinks Along With Battery Cost. By Nathaniel Bullard (Bloomberg Opinion: Technology & Ideas, April 12, 2019)
https://www.bloomberg.com/opinion/articles/2019-04-12/electric-vehicle-battery-shrinks-and-so-does-the-total-cost
You have been reading
Electric cars, vehicles, and hybrids are approaching and what you need to know
